What kind of information do your readers find important? How do they find your website? Are there any technical SEO issues that need fixing?
Google Search Console can answer all these questions and more. It’s one of the most powerful SEO tools out there—and it’s completely free.
So, why do so many online businesses overlook it?
One reason might be that Google Search Console can seem complex and a bit hard to navigate. But that’s no excuse to miss out on some major opportunities to boost your site’s visibility.
In this guide, we’ll break down the basics, show you how to use it, and help you get the most out of this fantastic tool. Plus, we’ll share tips from over 100 experts on how to use Google Search Console to increase your traffic and rankings.
What is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free tool from Google that helps you manage your website’s digital presence, fix technical SEO issues, and keep an eye on how well your site is performing in search results.
It’s a must-have because it provides the most current, real-time SEO data available. It’s amazing that such a powerful tool is completely free, giving you everything from tracking security issues to monitoring search performance and user experience.
For startups and marketers new to SEO, Google Search Console is an all-in-one solution that makes optimization and SEO management much easier.
Why is Google Search Console Important for SEO?
Google Search Console is the best tool for sharing important data with Google and optimizing your SEO. It offers unique features and detailed data that other SEO tools just can’t match, whether you’re focusing on technical aspects or content.
Here’s how you can use Google Search Console to boost your SEO:
- Track Key Metrics: Keep an eye on your average position, click-through rate (CTR), traffic data, keyword rankings, and organic traffic.
- Monitor Index Coverage: Ensure Google is indexing your pages correctly by checking your index coverage.
- Manage Sitemaps and Files: Handle your sitemaps, deletions, and disavow files.
- Check Core Web Vitals: Verify that Core Web Vitals and your overall page experience are up to par.
- Fix Mobile Usability Issues: Look into and address any problems with mobile usability.
- Review Manual Actions and Security Issues: Check for any manual actions or security concerns flagged by Google.
- Analyze Backlink Data: Examine important details about your backlinks, including anchor text, top linking pages and sites, and internal and external links.
All of these steps help you monitor, identify, and improve your SEO performance effectively.
Get Started with Google Search Console
A lot of SEOs hesitate to use Google Search Console because getting started can seem a bit confusing.
But don’t worry—we’ve broken down the setup into simple steps so you can get up and running easily. Here’s how to set up Google Search Console:
- Open an Account: Create your account.
- Verify Site Ownership: Prove that you own the site you’re working on.
- Add a Sitemap: Submit your sitemap to Google Search Console.
- Add a User: If needed, invite others to access your Google Search Console account.
Follow these steps, and you’ll be all set!
Set Up a Google Search Console Account
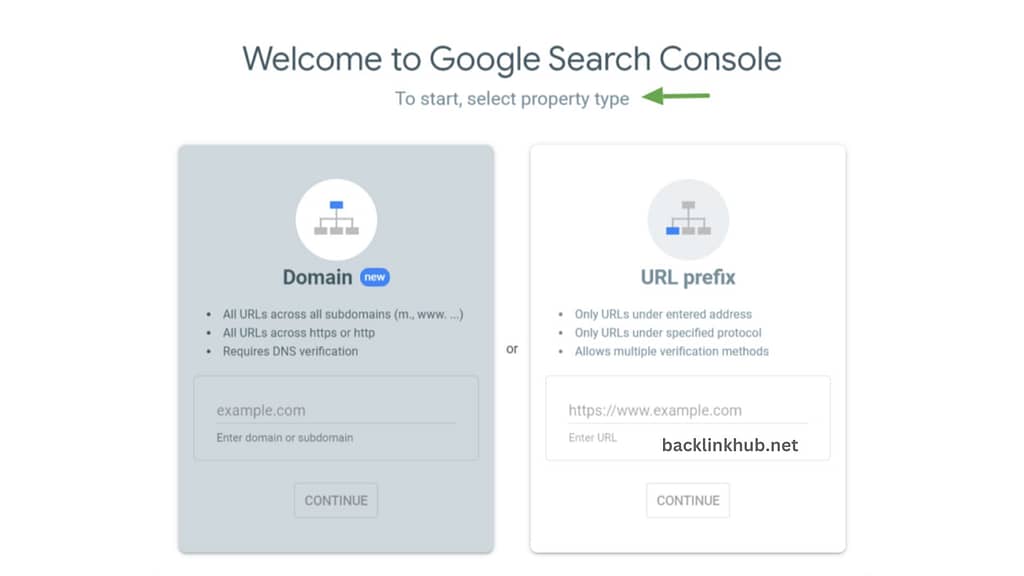
If you don’t have a Google Search Console account yet, head over to their official website to sign up.
Once you’re registered, add your website address in the domain or URL prefix tab (as shown below) and pick the type of property you’re setting up.
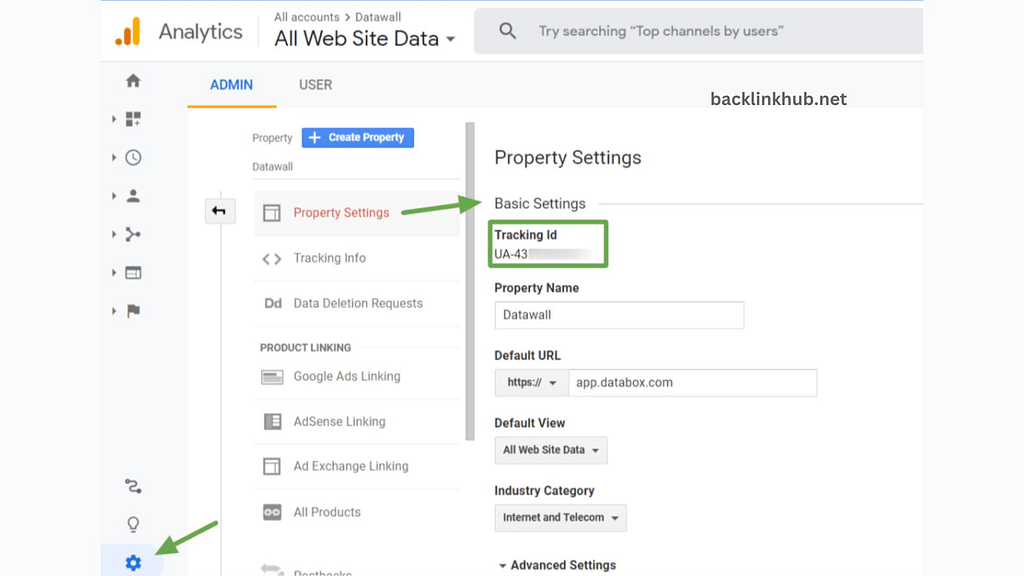
Finally, use your Google Analytics tracking ID to prove you own the website.
To find your tracking ID, go to Admin > Property Settings > Basic Settings > Tracking ID.
You can use the sidebar to access Google Search Console the next time you log into your Google Analytics account.
Verify Site Ownership
To get data from Google Search Console, you need to verify that you own the website. Besides using your Google Analytics tracking ID, there are two other methods depending on the type of property you added.
The first method is Domain Property Verification. Start by checking if your domain is registered with any of the listed services.
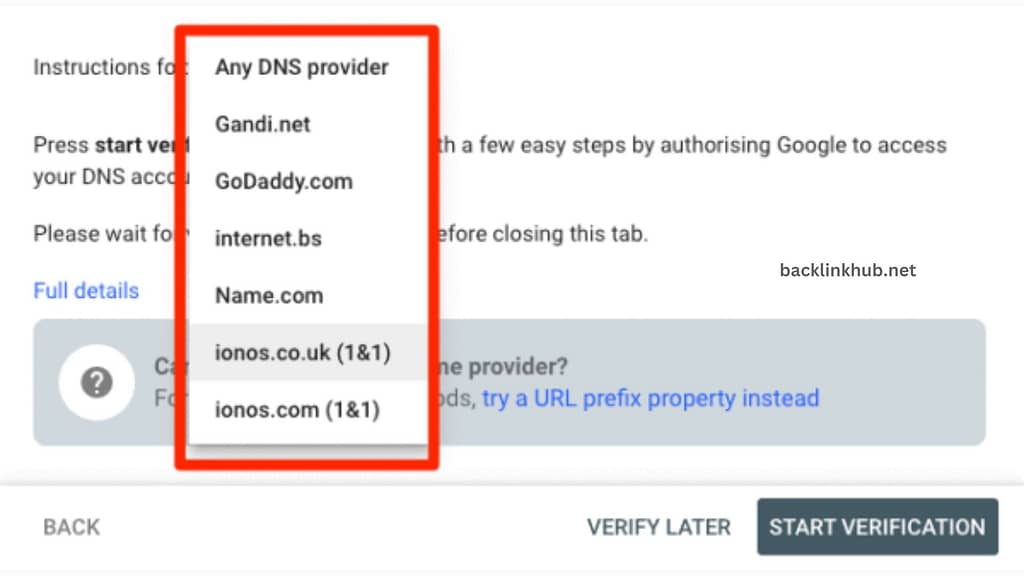
If you see your service provider listed, just select it and click “Start verification.” Then, log into your account and follow the instructions.
If you can’t find your provider, choose “Any DNS provider” instead. After that, pick your domain, log into your domain provider account, and look for the DNS (domain name servers) management option.
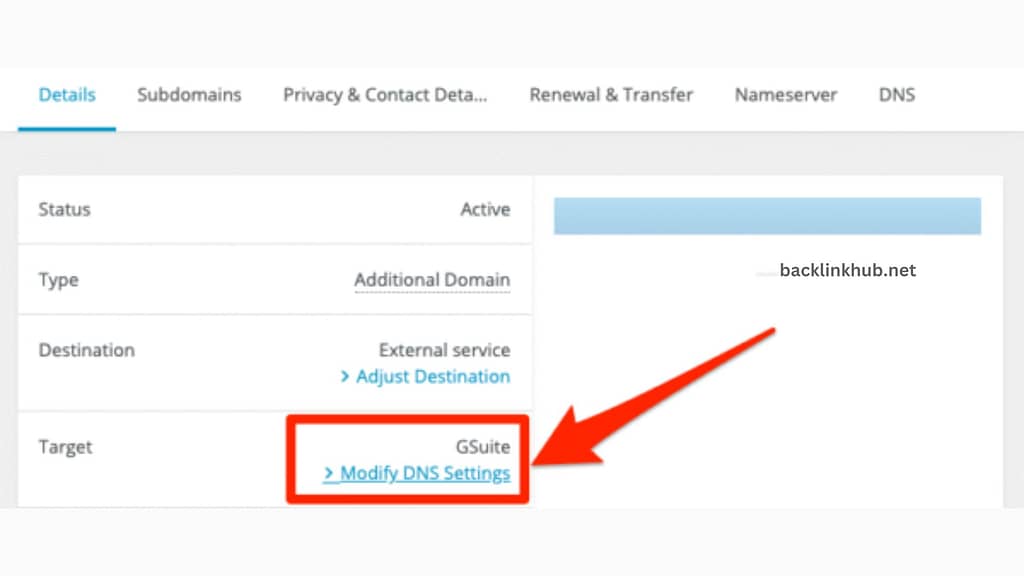
Once you’ve selected “Add TXT record,” copy and paste the record provided by Google Search Console. Save it and double-check to make sure it’s correct.
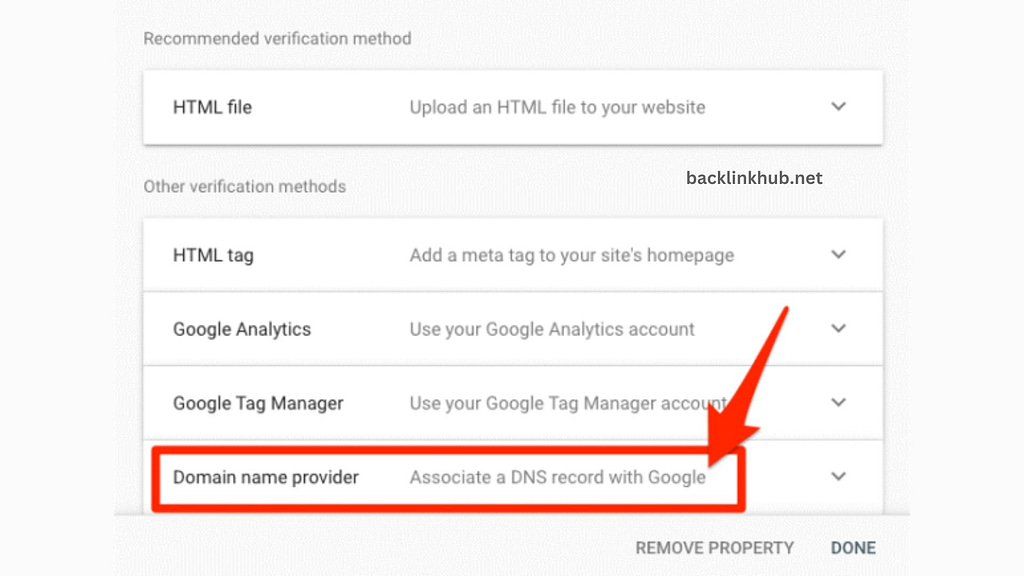
The second verification method is URL Prefix Property Verification. There are a few ways to do this, but the easiest method is to upload an HTML file to your website.
Add a Sitemap to Google Search Console
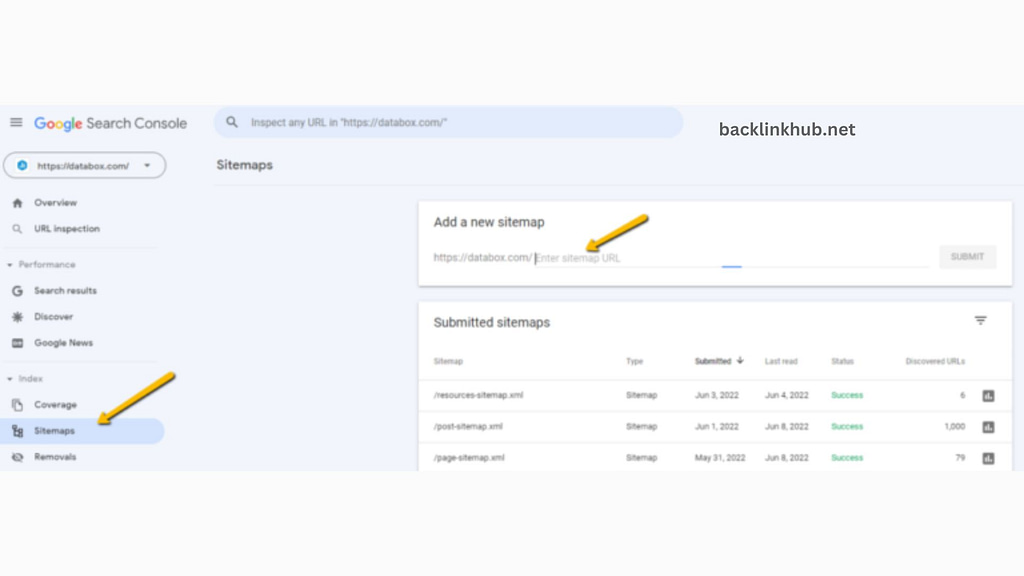
Adding a sitemap to Google Search Console is really important because it helps Google find and crawl the important content on your site more easily.
To do this, go to the “Sitemaps” section in Search Console, paste the URL of your XML sitemap into the “Enter sitemap URL” box, and then click “Submit.”
Add a User to Google Search Console
In Google Search Console, people who can see any or all of the data are called users. There are three types of users: Owner, Full, and Restricted.
When you verify a property, you become the owner. To add new users, go to Search Console, select your property, then go to Users & Permissions > Settings > Add User.
Enter their email address and choose if they should have restricted or full access. If you need to change or remove access later, you can always come back and adjust these settings.
Understanding Google Search Console Features and Reports
Google Search Console has a lot of useful data and tools for SEOs, but finding your way around them can be a bit confusing.
Let’s break down the different SEO reports and features you’ll find in Google Search Console and explain what they’re all about:
- Google Search Console Overview
- URL Inspection Tool
- Performance Report
- Index Report
- Experience Report
- Security Issues Report
- Manual Actions
- Links Report
We’ll cover each one so you know exactly how to use them to boost your SEO.
Google Search Console Overview Report
When you first log into Google Search Console, the Overview report is the first thing you’ll see.
Think of it as a snapshot of your website’s key data. It gives you a summary of important metrics like how many pages are indexed and if there are any manual actions taken against your site.
You can also click on links in this report to dive deeper into specific areas like Search Analytics, Sitemaps, and Crawl Errors.
The Overview report is great for spotting major issues and getting a quick sense of how your site is performing.
URL Inspection Tool
The URL Inspection Tool lets you see how Google views a specific page on your site.
If a page isn’t showing up in search results, this tool helps you check if Google has crawled or indexed it and can help you figure out what might be wrong.
It also highlights issues with HTML, JavaScript, and mobile usability, so you can let your development team know what needs fixing.
To use the tool, just copy and paste the URL of the page you want to check and hit enter. You’ll then see details about the page and whether it’s indexed.
Performance Report
The Performance Report gives you a lot of insight into how your website is doing in search engines.
In the first part of the report, you’ll see search features like featured snippets. You can explore four types of searches: Web, Image, Video, and News.
To switch from the default Web search to one of the others, just click on the “Search Type” option.
At the top of the Performance Report, you’ll see four key metrics:
- Total Clicks: This shows how many times people clicked on your website from search results.
- Total Impressions: This is the number of times your website appeared in search results.
- Average CTR: This is the average percentage of people who clicked on your site out of those who saw it in search results.
- Average Position: This tells you the average ranking of your website in search results.
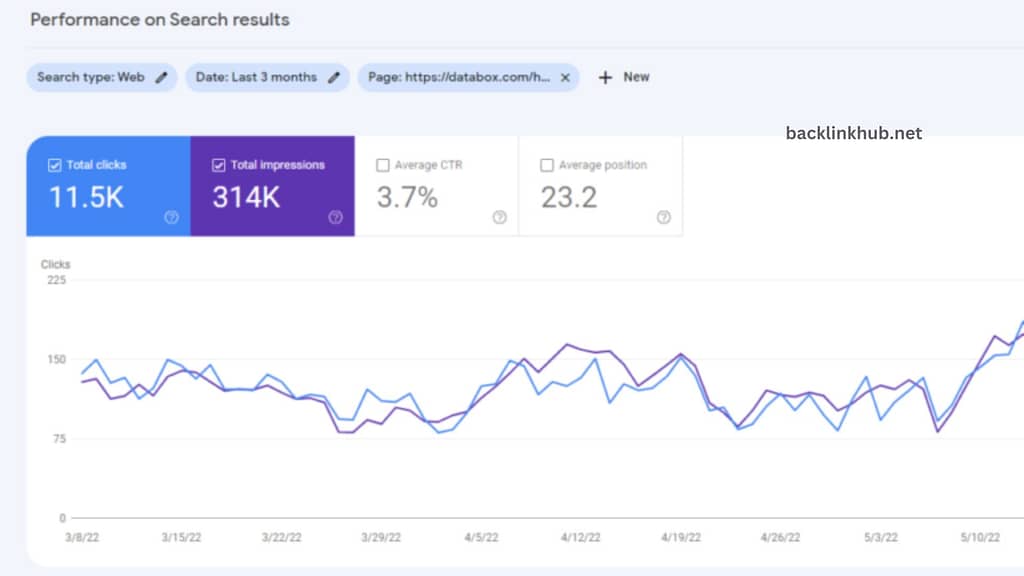
At the bottom of the Performance Report, you can explore six different types of performance data:
- Queries: See which search terms and keywords are bringing people to your site.
- Pages: Check out which of your pages are ranking the highest.
- Countries: Find out which countries are sending the most traffic to your site.
- Devices: See what devices people are using to visit your site (like desktop, tablet, or mobile).
- Search Appearance: Look at the different types of search results where your site appears.
- Date: This section shows impressions and clicks sorted by date.
Index Report
The Index Report shows if Google is crawling your site and if there are any problems preventing your pages from being indexed.
When you open the report, you’ll see a simple chart that shows how the number of indexed pages has changed over the last 90 days.
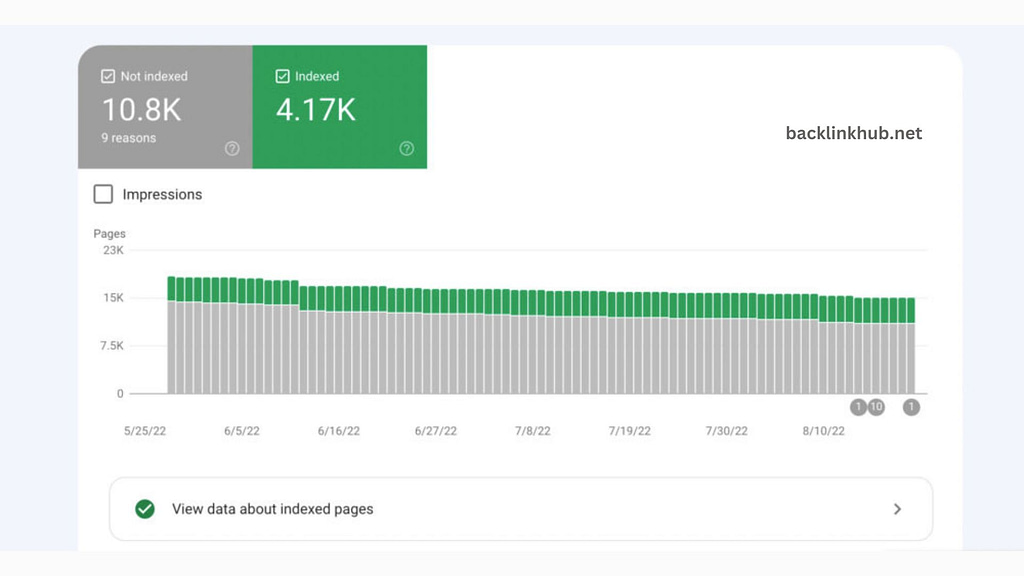
The report uses four colors to show different statuses:
- Red – Error
- Yellow – Caution
- Green – All good
- Gray – Not included
Since errors are the biggest hurdle to getting your content indexed, you should tackle those first.
Also Read: How to Optimize for Local SEO
Experience Report
The Experience report gives you insights into how visitors are experiencing your website.
It shows how Google evaluates the user experience of specific pages on your site, which affects how those pages rank in search results.
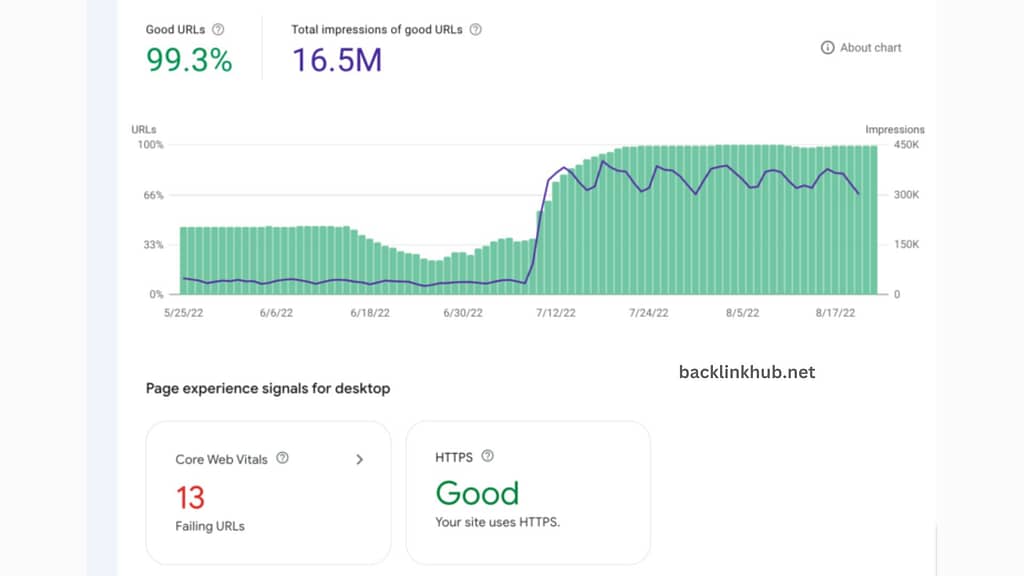
Here’s how Google assesses your site:
- Core Web Vitals – This checks how well your pages load, how stable they are, and how responsive they are. Your site gets rated as Good, Needs Improvement, or Poor.
- Mobile Usability – For a “Good” rating on mobile, your pages need to work smoothly on mobile devices without any issues.
- HTTPS Usage – To get a “Good” ranking, your pages must use HTTPS, which means they’re secure.
Security Issues Report
The Security Issues report shows if Google has found any signs that your website might be hacked or acting in a way that could harm visitors.
Google uses “acting suspiciously” to cover things like phishing scams or malware that could be infecting visitors’ devices.
When someone tries to visit your page and finds a security problem, they’ll usually see a warning either in the search results or on a warning page.
There are three main types of security issues:
- Hacked Content – This is when unauthorized content is added to your site without your permission.
- Malware/Unwanted Software – This includes harmful software that can damage a visitor’s device.
- Social Engineering – This involves dangerous content that tricks visitors into doing something risky, like sharing personal information.
Manual Actions
This report tells you if your website has been hit with any manual penalties.
In other words, it checks if any of your pages are breaking Google’s quality guidelines, which could lead to them being hidden from search results.
If any manual actions do affect your pages, you’ll get a notification in the Search Console message center.Links Report
The Links report shows all the links pointing to your website. However, it doesn’t include links that help your site’s search engine ranking. Instead, it focuses on links that might hurt your SERP ranking.
In the report, you’ll find separate sections for internal and external links. For external links, there are three reports: Top Linked Pages, Top Linking Sites, and Top Linking Text. For internal links, there’s just one report called Top Linked Pages.
You can click on any of these reports to see more details. For example, by expanding the Top Linked Pages report, you can see which pages on your site are linked to the most.
How to Use Google Search Console for SEO: 20 Pro Tips
Now that we’ve covered the basics of Google Search Console, let’s dive into some expert tips from the SEOs we talked to.
Here are some of the best Google Search Console tips from over 100 marketers we’ve interviewed.
Use Search Console for Keyword Research
The Performance Report in Google Search Console gives you essential SEO information. It shows you the search terms, called “queries,” that your website and pages rank for.
To start exploring keywords with Google Search Console, sign in, click on Performance, and then go to the Queries tab at the bottom of the page.
The Queries tab will be open by default. From there, you can scroll through the list to see all the keywords that your website shows up for in search results.
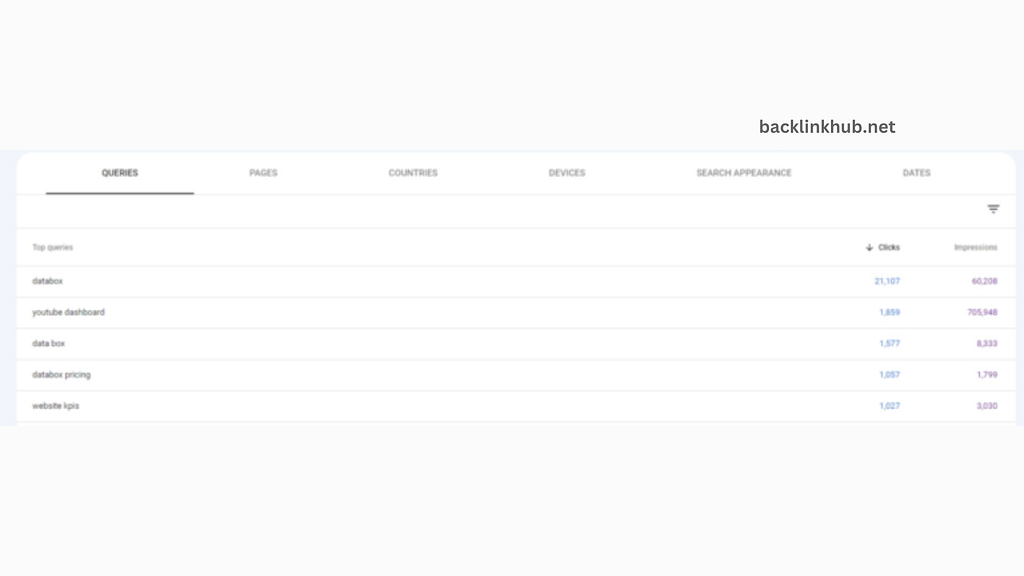
You’ll need to take a few more steps if you want to check what keywords each of your individual pages ranks for. Select the page you wish to review by first clicking the Pages tab.
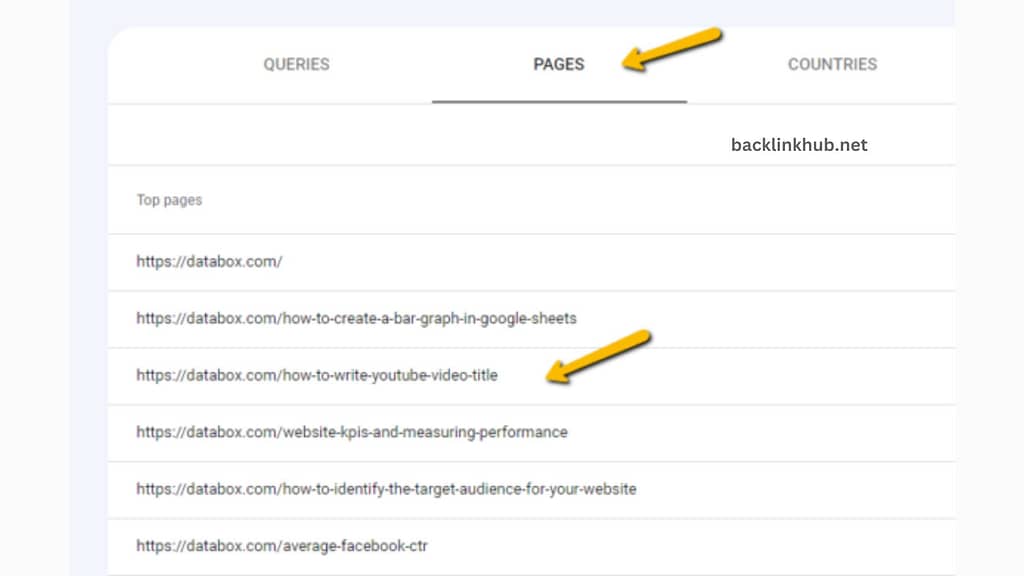
Click the “Queries” tab once more now. This is where you can view every term that the particular page you chose in the previous step ranks for.
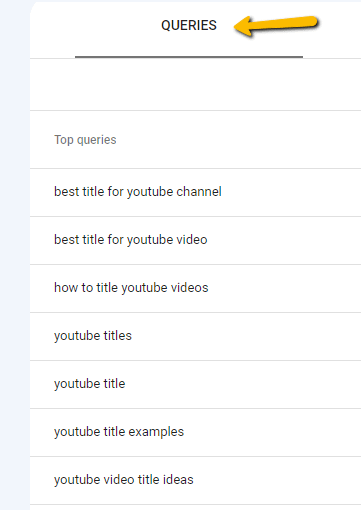
To check the keywords for a different page, go back to the Pages tab, pick the page you want to view, close the current page, and then click Queries again.
You can also use Google Search Console’s keyword tool to boost your local SEO.
Tony Mastri from MARION Marketing Agency does it this way:
“I usually add a URL query to the GMB primary website field, then use Google Search Console to see what keywords people are using to find and choose my local listings,” Mastri says.
“You can use the Exact URL page filter in GSC to separate standard and local organic clicks to a page. This gives you detailed search phrase data that can really help with local SEO efforts.”
Check Your Average Position for Specific Queries
Another important metric in the performance report is the average position. This tells you where your website ranks for specific search terms.
If you’re ranking in the top results, you’re in position one. If you’re on page two, you might be around position 11.
The average position is calculated by adding up your rankings for all keywords and then dividing by the total number of keywords.
While it’s not the only measure of your site’s health, a good average position in GSC is generally around 30 or lower.
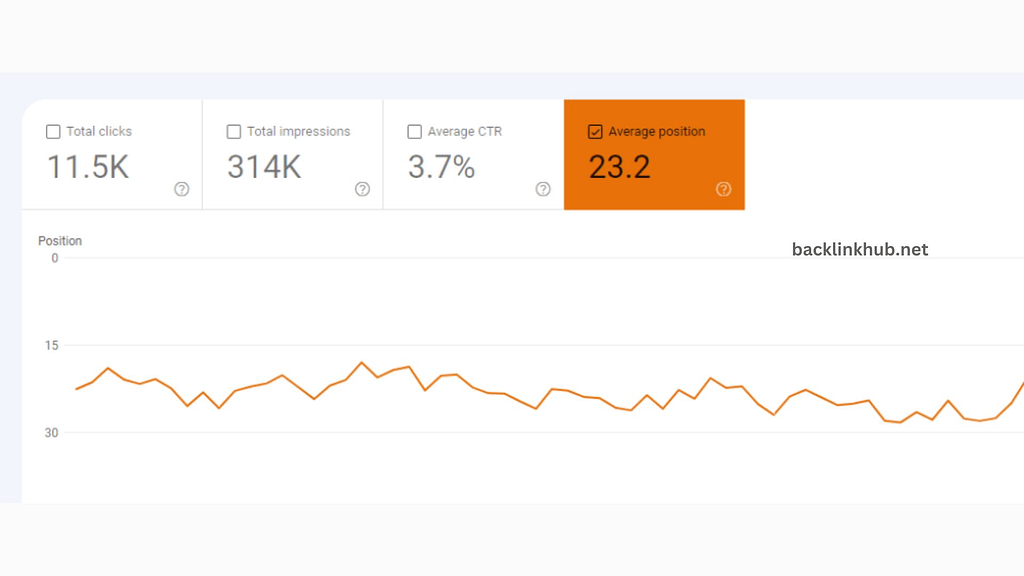
In the general report, you’ll see the average position for all the keywords your website ranks for. If you filter by page, it shows the average ranking for each keyword that specific page targets.
However, the average position isn’t always the most helpful metric. For more detailed insights, scroll down to the table below the graph. There, you can see how you rank for each specific keyword, which can give you more useful information.

With the help of this data, you can track changes in your rankings following on-site modifications and optimizations in addition to seeing precisely where each page of your website ranks for particular keywords.
Check for Website Coverage Issues
You can find out exactly how many pages of your website Google has indexed by using the Coverage Report feature of Google Search Console.
To view the data, click Pages in the index report.
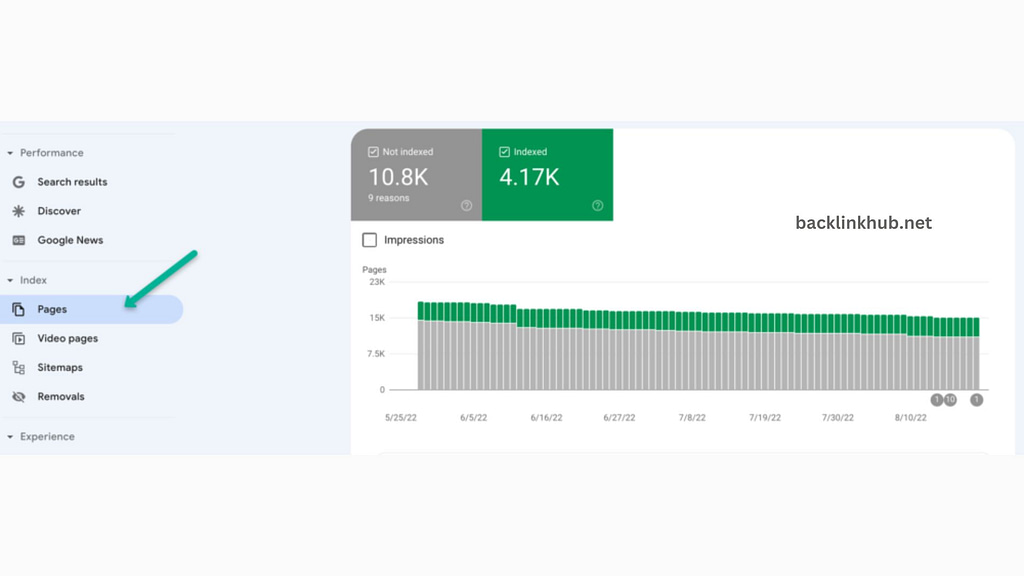
For larger websites, it’s a good idea to compare the number of pages listed in your XML sitemap with the number of pages Google has actually indexed.
This check is key to spotting any issues with crawling, indexing, or content duplication on your site.
If you notice a page missing from Google’s index, you can use the URL inspection tool to request that Google index it.
Just click on the tool, paste the URL you want to check into the search field, and wait for Google to analyze it. If no problems are found, click “Request Indexing” to have Google add it to their index.
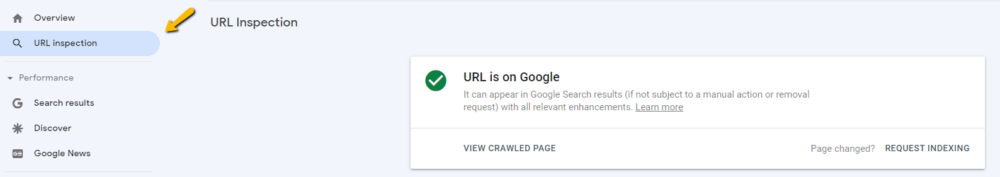
The time it takes Google to process your request, crawl the website, and index it could range from a few hours to several days.
Identify Crawl Errors and Unindexable Pages
Sometimes, developers use canonical or no-index tags to stop Google from scanning certain pages, but they might forget to remove these tags later. Similarly, you might delete a page without setting up a proper redirect.
The good news is that Google Search Console tracks these issues for you, so you don’t have to sift through every page’s HTML code yourself.
To find these problems, just click on “Pages” in the Index report and review the details. Google Search Console will help you understand why certain pages haven’t been indexed.
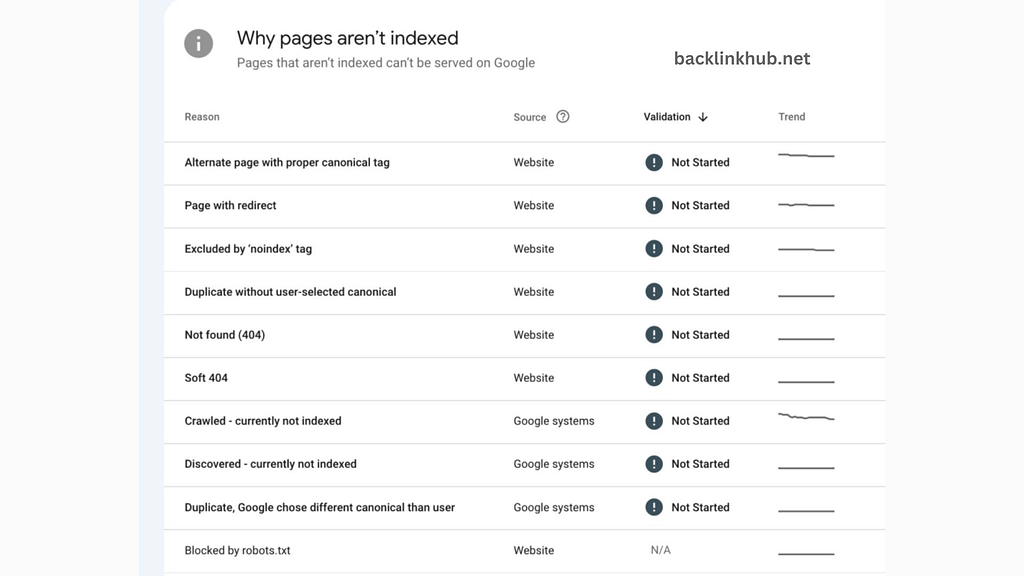
The Page Indexing tool in Google Search Console not only shows you which pages aren’t indexed but also explains why. It can help you spot different issues, like indexing mistakes made by developers, 404 errors, and more.
Sometimes, Google might have indexed broken or outdated links, which often lead to 404 errors. With this tool, you can easily find the URLs on your site that are causing these errors.
Optimize Your Website Pages for Mobile Search
With Google’s shift to mobile-first indexing, it’s more crucial than ever to make sure every page on your site is mobile-friendly.
Luckily, Google Search Console makes it easy to spot any issues with your mobile pages. Just click on “Mobile Usability” to see if there are any problems. If there are, you can find more details by continuing to read the page.
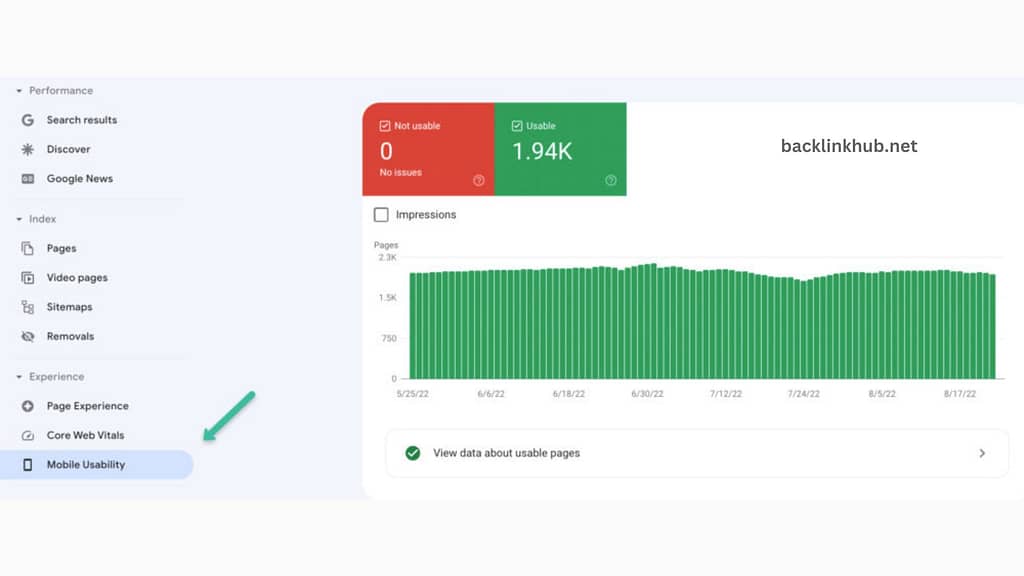
Google Search Console makes it easy to check if your website’s pages load quickly, work well on mobile devices, and have everything in place correctly (like ensuring fonts aren’t too small for mobile screens).
The best part? It also tells you what needs fixing. This way, your visitors will have a smoother experience on your site, and your pages will rank better in search results.
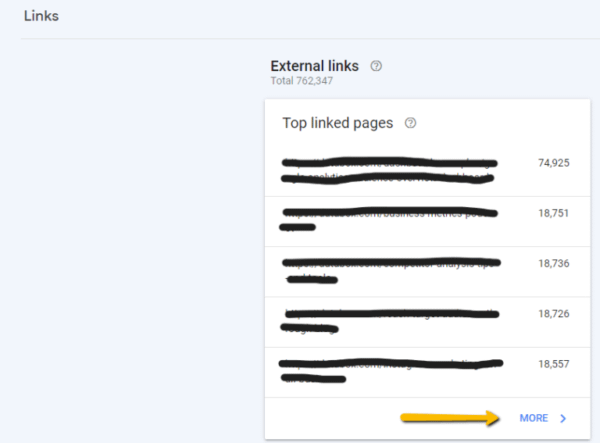
Check Your Backlink Profile
The Links Report in Google Search Console shows which websites are linking to yours, which pages on other sites are linking to yours the most, and which of your pages have the most links.
To see all your inbound links, click on the “Links” tab and then hit “More” under “Top linking sites.” This will show you all the backlinks pointing to your website.
See if Your Site Has Any Penalties
If Google finds that your site isn’t meeting its quality standards, it might take manual action against it, which could even lead to your site being removed from the index.
Manual actions often result from practices like keyword stuffing, deceptive redirects, buying backlinks, or using low-quality or scraped content.
If you or someone you hired has used questionable methods to boost your SEO, it’s a good idea to check if you’ve received a manual penalty.
But remember, you might also get a manual penalty for issues you didn’t cause. For instance, if your site gets hacked or if there are lots of spammy comments with links to shady websites, Google might penalize you.
Ideally, you won’t face any manual penalties, but if you notice a sudden drop in traffic and can’t figure out why, check the “Manual actions” report. If there’s an issue, the report will provide guidance on how to fix it and get your site back in Google’s good graces.
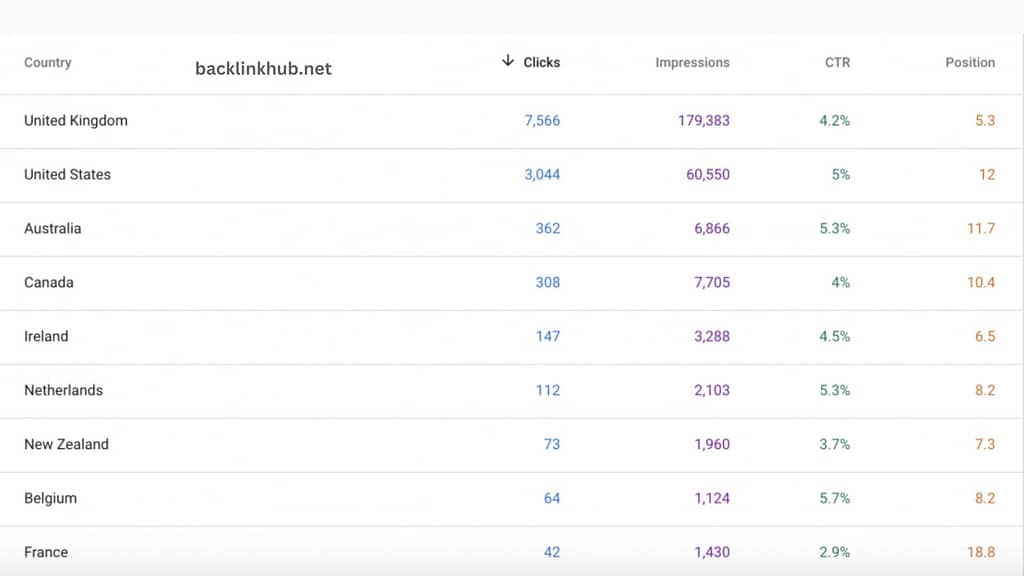
Use International Targeting Report for Prioritizing a Specific Country in Search Results
In Google Search Console, you can use the “Country” tab in the International Targeting report to focus on specific countries for your search results.
This is important because someone in Greece might see different search results than someone in the UK.
If you have a generic domain like .com or .org, it helps Google understand which countries matter most to you. But if you’re using a country-specific domain, like .fr for France, your site is already linked to that country, so you can’t specify a different one.
Anjana Wickramaratne from Active Digi Solutions suggests, “To get the most out of Google Search Console, keep an eye on the ‘Countries’ tab to see where your results are showing up.”
“While it’s useful to track the queries your site ranks for, it’s also important to know which countries you’re ranking in.” By watching which countries show up in your search results, you can adjust your SEO strategies to better target the locations you care about.
Analyze Mobile vs. Desktop Traffic
To stay ahead, you should focus on optimizing both desktop and mobile traffic.
Even though mobile searches now make up 64% of all searches compared to 36% on desktops, many businesses still focus mainly on desktop traffic.
Finn Hayden from You Well recommends checking the devices listed in the performance report. Many companies forget that mobile devices often drive the majority of their traffic, and mobile search results might differ from desktop rankings.
“The Devices section in Search Console’s performance report shows which devices are bringing the most visitors to your site,” Hayden says.
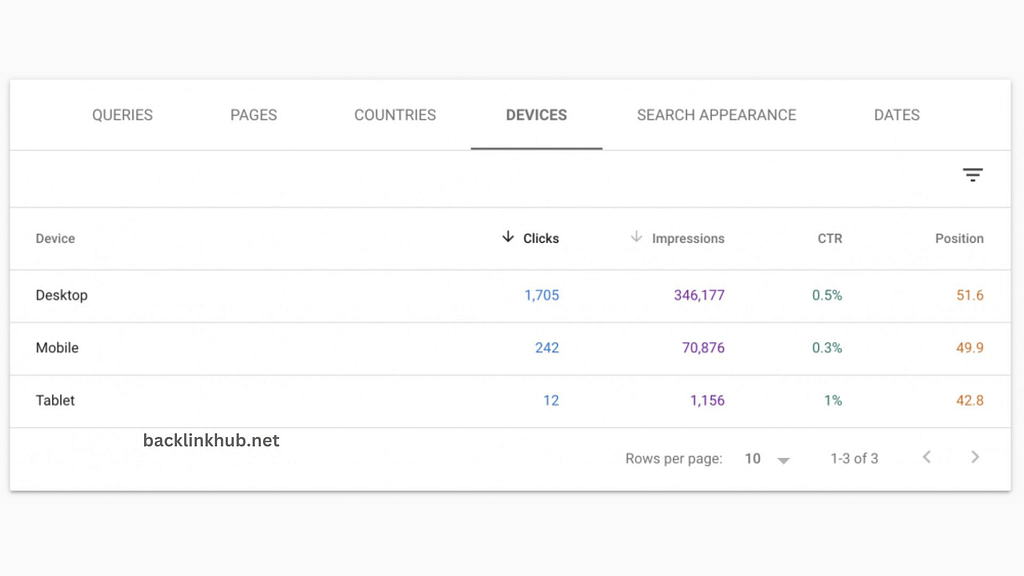
“You can pull out some great reports from here that will really help show you if your SEO work is effective,” says Hayden in his explanation. For instance, if your SEO is effective, you ought to notice a steady rise in mobile traffic.
Prevent Keyword Cannibalization Issues
When your website has too many pages with the same or similar keywords, Google gets confused about which page should rank higher. This is known as “keyword cannibalization.”
It becomes a problem when a page you didn’t intend to prioritize ends up ranking higher.
Kiera Lavington from Candour suggests using the Performance Report to spot possible keyword cannibalization. Start by filtering the queries for your target term. Look at which pages show up for that term and use the “Compare” option to see how the top two pages (based on impressions) stack up.
“Check the ‘Impressions’ or ‘Average Position’ tabs to see how pages moved in and out of search results for the target phrase,” Lavington explains.
“If you notice that one page starts ranking while another drops, you’re on the right track, but you may need more investigation to confirm a cannibalization issue,” she adds.
Check the Canonical Domain Settings
The canonical domain is the version of your website that you want Google to prioritize for indexing.
Google uses this information to decide which domain to index and to handle duplicate content properly.
Tomas Hoyos from Voro recommends making sure you choose your preferred canonical domain in Google Search Console. In other words, decide if you want your domain to have “www” in front of it (like www.voro.com) or not.
If you don’t set a canonical domain, Google might treat the “www” and non-“www” versions of your site as separate. This means you’ll have to share the credit for clicks, page views, backlinks, and engagement between the two domains, which could hurt your SEO, Hoyos warns.
Change Meta Tags and Monitor the CTR Impact
Meta tags are the text snippets that appear under your article’s title in search results. They give a brief summary of what the page is about and help Google understand the content. These tags are part of your website’s source code but don’t show up on the actual page itself.
Since these snippets play a big role in off-page SEO, it’s a good idea to try different meta tags and see how they impact your click-through rate (CTR).
Nick Swan from Sanitycheck explains, “We always keep an eye on the CTR for our top keywords and pages. Our data shows that as we improve our CTR, our rankings tend to get better over time.”
Each month, we check if our updated content boosts our CTR and tweak our title tags and meta descriptions as needed. Testing these elements is as important as testing ad copy for Google Ads.
Monitor High CTR Keywords and Optimize Content Around Them
To find keywords worth optimizing, keep an eye on those with a high click-through rate (CTR). For instance, even if one keyword has a lower search volume than another, it might be more beneficial if it attracts more clicks.
Lynn Hericks from Intuitive Digital suggests, “Focus on optimizing and expanding older blog posts using keywords that are already performing well.”
In Google Search Console, you can find keywords that rank around positions 8–20 by filtering your searches by page in the Performance section. These are terms your content is showing up for, even if you didn’t target them directly.
“Go back and update your blog post to include these keywords and expand the content to boost your rankings,” advises Hericks.
Parker Short from Pyxis Growth Partners recommends using Google Analytics to find your most visited pages, then using Google Search Console to gather the info needed to improve them further.
“Look at the terms each page ranks for, especially those in positions #2–10. Try to naturally include these terms in your content,” says Short.
“This is a great way to optimize older blog posts and attract more organic traffic,” he adds.
Find Exploding Topics
You can use Google Search Console to spot new trends and see where fresh traffic is coming from. If you’ve just published a new article or added a new product category, check out the Search Results performance report. Filter it to the most recent dates to see the latest organic search traffic.
By looking at metrics like impressions, CTR, and average ranking, you can predict where future traffic might come from. This helps you audit your keyword targeting, refine your content, improve internal links, and more.
Here’s how TJ Kelly from RaySecur, Inc. does it:
- Go to your performance report.
- Click on the Pages tab.
- Sort by Impressions to see which pages are showing up the most in search results.
- Pick one of your important pages.
- After the report updates, click on the Queries tab.
- Adjust the date range to compare the last three months with the previous period, then click Compare.
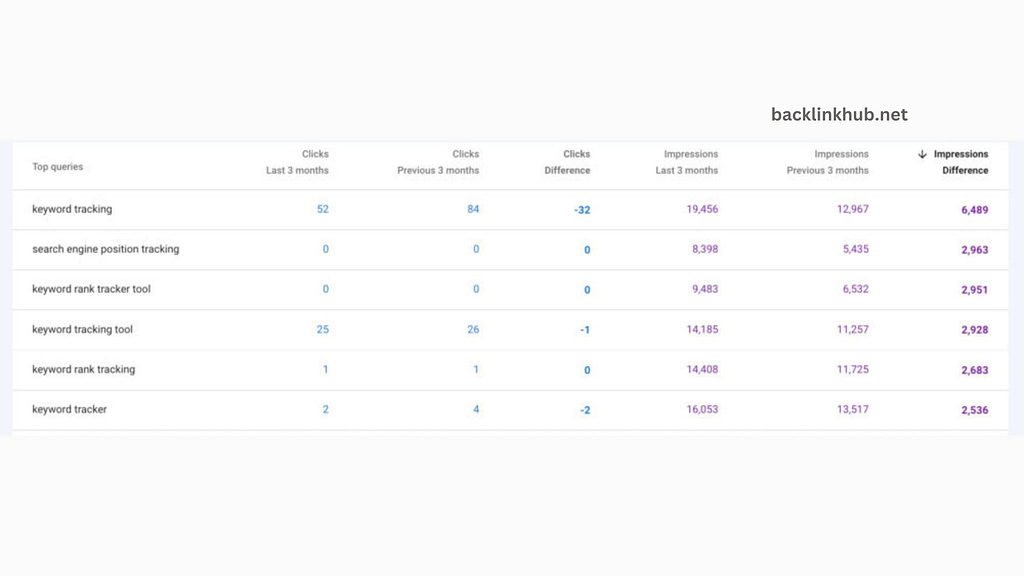
As Kelly puts it, “By sorting your data by Impressions for both the Last 3 Months and the Previous 3 Months, you can see which queries are driving more or fewer search impressions for a particular page.”
The trick is to spot queries that are getting a lot of impressions in the last three months but had fewer in the three months before. This could indicate that new queries are ranking higher or getting more search volume, opening up new traffic opportunities.
Kelly suggests exporting the report to a spreadsheet, calculating the changes, and sorting by these changes. “This helps you see which queries have had the biggest jumps or drops over time.”
To get a full picture, compare this data with your click-through rate. If impressions are increasing but your click-through rate is flat, it might mean your rankings are slipping.
Find Internal Linking Opportunities
Google Search Console is great not just for checking your link status but also for spotting good internal linking opportunities.
Faizan Ali from WPBeginner suggests, “One useful tip is to use GSC to find pages that could use more internal links. Just click on ‘More’ under the top linked pages, then look at the internal links to see which pages need them.”
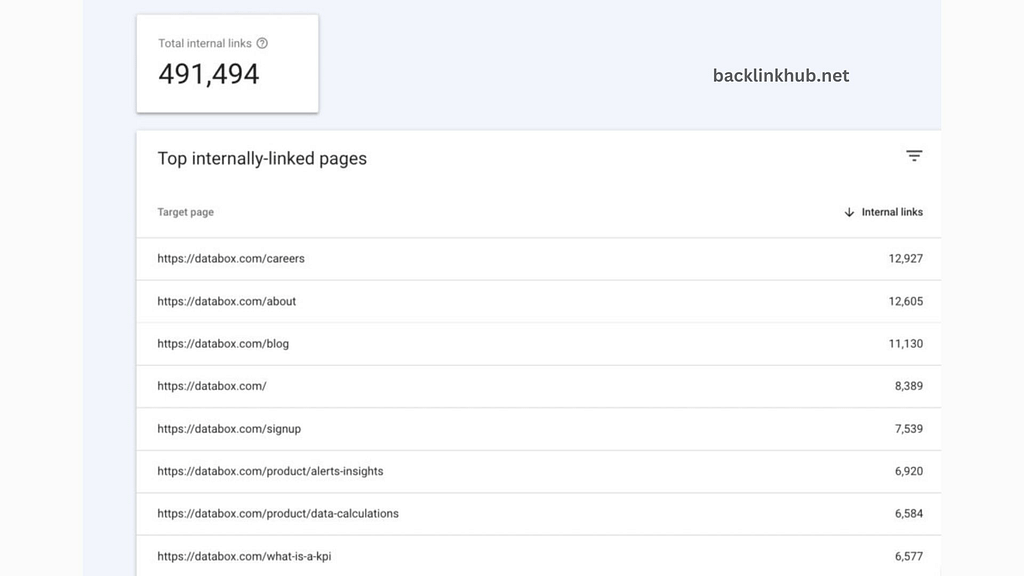
“Internal linking has two big benefits,” says Ali. “First, it can help your new pages get indexed by Google faster. Second, it passes PageRank to the new pages, which can boost their rankings in search results.”
Ali also suggests using the search operator site:yourdomain.com 'keyword you wish to internal link' to find good internal linking opportunities.
To keep improving, make sure you set up a regular process for internal linking based on the chances you discover.
Compare Your Search Performance to Previous Periods
One of the most important but often overlooked features in Google Search Console is tracking your web performance over time. This data can reveal whether your SEO strategies are working or if you need to try a new approach.
Deniz Doganay from Digital Debut says, “I really like comparing quarterly performance year-over-year in the performance section.”
This comparison can provide valuable insights, like how your rankings, clicks, and impressions have changed. You can even get a good estimate of your click-through rate (CTR).
Doganay adds, “Even if your impressions and rankings have improved, your CTR might be lower. If that’s the case, you might need to improve your calls to action (CTAs), meta titles, and descriptions, or review what you’re doing on other channels.”
How to Use Google Search Console for Link Analysis
PRO TIP: Want to track your organic search and see which landing pages and keywords are performing the best? Use Google Search Console, Accuranker, and Databox to pinpoint the topics and keywords that can boost your content marketing strategy. These tools will help you optimize your approach and get the best results.
Determine Which Pages Are Wasting Your Crawl Budget
Google doesn’t always visit every page on your website. Sometimes, it sets a crawl budget, which limits how many pages it will crawl regularly.
This can be a problem because Google might miss new or updated content, which means it won’t show up in search results.
For smaller sites, this usually isn’t an issue. But if you have a large site with thousands of pages, it can become a problem. Google notes that having a lot of low-value pages can hurt how well your site is crawled and indexed.
Martin Woods from Indigoextra suggests using Google Search Console to spot low-value pages that might be wasting your crawl budget. “Google Search Console is excellent for finding pages that aren’t getting any visits,” he says.
To do this, look for pages with the fewest impressions and clicks. You can then choose to remove these pages, redirect them to more valuable pages, or improve their content.
Research shows that removing or redirecting low-traffic pages can make Google focus more on the relevant pages, boosting overall traffic to your site, according to Woods.
Decrease Your Bounce Rate by Identifying Negative Keywords
Sam Makwana from Traffic Radius explains, “One great thing about using Google Search Console is that it helps you spot negative keywords—those terms your site shouldn’t be ranking for.”
Negative keywords are phrases where your content doesn’t match what users are looking for. Makwana points out that this mismatch can hurt your bounce rate, which is the rate at which visitors leave your site quickly. “You can lower your bounce rate by fixing these issues.”
One way to fix this is by updating your content to better match the keywords you’re already ranking for but haven’t fully covered. Another approach is to create a new post that addresses the topic of a negative keyword and link it from an existing post that ranks well for that term.
Give Google More Information About Your Site without Adding Structured Data
Google can learn more about your website content when you use structured data. Structured data helps Google identify what type of content you have, whether it’s an article, FAQ, recipe, job posting, review, or something else.
Using structured data can make your search results more detailed and improve how Google understands your content. For example, a search result with structured data for ratings and recipes can provide more information when clicked.
However, as John Hodge from Primitive Social says, “Not all SEOs know web development, and even those who do might not have access to the website’s code.”
Google Search Console’s data highlighter lets you change how your website appears in search results. This can boost your rankings, make your pages stand out, and give Google more context about your content.
The data highlighter is easy to use and doesn’t require adding structured data to your site’s code. Just choose the item (like software, reviews, or restaurants), enter the page’s URL, and start highlighting.
You can specify more details about content, such as images, official URLs, and download links, when you highlight it. Google uses these contextual cues to determine item rankings, so using the data highlighter is a quick and effective way to improve your website’s content.




Pingback: Overcoming Broken Link Challenges