Got hit with a Google penalty?
You’re not alone.
Google hands out over 400,000 manual penalties every month, and that doesn’t even count the penalties from changes to their core algorithm.
But here’s some good news:
You can recover from a Google penalty.
It’s not an easy process, though. You need to be committed and follow the right steps to get the results you want.
In this blog post, I’ll walk you through my four-step method for recovering from a Google penalty.
Let’s dive in!
Identify What Penalty Hit Your Site Before To Make Any Changes
The first step to recovering from a Google penalty is figuring out what kind you got.
There are two types of Google penalties:
- Manual
- Algorithmic
What you need to do depends on which type of penalty you’ve received. Each one requires a different approach—or sometimes a mix of both—to fix.
Were You Hit By A Manual Penalty?
Google’s webspam or search quality team hands out manual penalties. After reviewing your website, they decide to manually penalize your site.
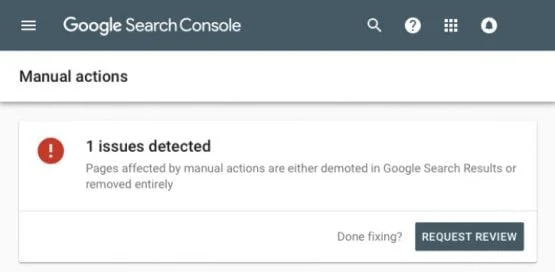
Manual penalties usually come from:
- Unnatural links to or from your site
- Spammy content or pages
- Manipulative structured markup
- Cloaked images and redirects
If you’ve been hit with a manual penalty, Google will let you know through Google Search Console.
Were You Hit By An Algorithmic Penalty?
In case you didn’t know, Google search is powered by an algorithm.
This algorithm, which is basically a bunch of complex math formulas, decides which results show up for users.
Unlike manual penalties, algorithmic penalties are triggered automatically by Google’s search algorithm. The two main algorithmic penalties to watch out for are:
- Google Panda penalty
- Google Penguin penalty

Since its launch in 2011, Google Panda has become a key part of the Google algorithm, focusing mainly on content issues.
It targets things like pages with very little content or those with too many ads compared to the actual content.
When Google Penguin came out in 2012, it caused major problems for many websites. Its main goal is to target sites that use shady links to boost their rankings.
That’s why it’s important to create high-quality links or work with trustworthy link-building companies that focus on quality.
How To Recover From A Google Penalty Step By Step
Think Google has penalized you?
Just follow my step-by-step guide to recover from Google penalties. I’ve used this exact method with our clients and helped many businesses bounce back quickly.
Here’s how it works.
Step 1: Examine Potential Ranking Issues
Before you take any action, you need to understand what’s going on.
If you keep searching blindly for the “right fix,” you won’t get very far.
Start by checking these sources for any potential ranking issues.
Google Analytics Check
First, check Google Analytics to make sure your tracking code is set up correctly.
You’d be surprised how often this turns out to be the problem.

Use the Google Analytics Debugger add-on to make sure everything is working right.
Manual Penalty Review
To see if your website has a manual penalty, go to Google Search Console. Click on “Security & Manual Actions,” then select “Manual Actions.”
Look for any error messages in this section.

If you find that a manual penalty is the problem, consider hiring an expert SEO agency to help. Dealing with manual penalties can be tricky.
Google Search Console Error Check
Check Google Search Console for any reported issues.
Go to “Indexing” and click on “Pages.”

Any coverage problems will be listed here.
Next, review your site’s user experience.
Click on “Experience” and look through the following reports:
- Page Experience
- Core Web Vitals
- HTTPS

Don’t worry if you find any issues.
Just fix each problem and submit the corrected versions for verification. Any major errors causing penalties should be listed in Google Search Console.
Recent Site Changes
Can’t find the problem?
Ask every team member (or developer) if there have been any major site changes in the last three months.
You might be surprised at how much these changes can affect your site.
Important: If you discover errors, stay calm.
Panicking can lead to rash, emotion-driven decisions. Make decisions based on data. Continue with the rest of the steps in the process.
Also Read: Editorial Links: What They Are & How to Get Them in 2024
Step 2: Look Into Recent Algorithm Updates
Google frequently updates its algorithm.
A drop in traffic and site performance might be due to one of these updates. Sometimes, you might even get penalized.
So, it’s important to:
- Stay updated on Google algorithm changes
- Act quickly if needed
Moz has a helpful page that tracks all Google updates as they happen. Check their page to see if any updates match the time when your website’s performance declined.

Found a connection?
Look at who the update targets and adjust your website accordingly.
There are many tools available to help you figure out which updates have affected your site and why.
Use a Google penalty checker tool to analyze the updates and find solutions.
Step 3: Run A Complete SEO Audit On Your Site
It’s time to review your website and find any issues.
You need to do two audits:
- SEO audit
- Content audit
This will help you identify any problems that might have caused a Google penalty.
Complete An SEO Audit

Every six to twelve months, you should do a thorough SEO assessment of your website.
Here’s the thing:
Conducting a true technical SEO audit can be tough unless you have substantial SEO knowledge. It requires expertise that professional SEOs typically have.
If you’re not confident, consider getting help from a reputable agency.
Ready to do your own SEO audit? Follow these five steps:
- Listen to your visitors – Conduct a survey to get feedback from your users.
- Manually observe problems – Examine your website to identify areas where the user experience could be improved.
- Perform technical spot checks – Do a quick technical SEO assessment to find any technical issues that need attention.
- Scan your site with an SEO audit tool – Use a high-quality SEO tool to perform a site assessment.
- Create a plan of action – With all the information gathered, create a plan to implement the necessary changes.
Complete A Content Audit
Your company’s online image is shaped by its content.
Good content helps your business grow, while poor content can hurt your reputation. A content audit helps identify issues with:
- Quality
- Relevance
Both are crucial for ensuring your content supports your website and business growth.
For content audits, I use Surfer SEO. Their SERP analyzer will:
- Analyze each URL
- Audit your content
- Suggest improvements
Pretty cool, right?
Surfer SEO does the hard work. All you need to do is follow the suggestions.
Step 4. Clean Up Your Backlink Profile
If you want to recover from a Google penalty, improving your link profile is crucial.
Here’s how you can do it yourself.
Find And Identify All Your Bad Links
To find and remove harmful backlinks, you’ll need to do a backlink audit.
Here’s what you’ll need:
- Google Search Console
- Moz
First, log in to your Google Search Console account. Click on “Links” in the left sidebar to see a list of all the domains linking to your site.

Google Search Console doesn’t show every link to your website. To make sure you have the complete picture, use another SEO tool to cross-check.
Try the Moz Open Site Explorer tool for additional backlinks. Just sign up for a free account and add your domain to get started.

Now, export the list of links from Moz. You should have two lists of backlinks at this point.
The final step is to go through each link and spot any that are problematic. Make sure you use the right tool for this job.

Enter Monitor Backlinks and upload both of your backlink lists.

Along with the lists you recently supplied, Monitor Backlinks leverages Ahrefs API and Google Analytics to locate additional links, so you won’t miss a single one.
To be ready to eliminate the problematic links, use Monitor Backlinks to assess each link.
Use my how to remove poor backlinks guide if you need additional assistance identifying and eliminating harmful backlinks.
Request Removal Of The Bad Links
After compiling a list of links you wish to delete, you must contact the owners of each website and request the links be taken down.

To get the site owner’s name and email address, use a service such as Hunter.io.

I suggest using a program like BuzzStream if you need to contact a lot of site owners. Sending automated follow-up emails and keeping track of every email sent is really simple with it.
A word of caution: When requesting the removal of a link, be kind and kind. Being courteous will go a long way because the site owner is assisting you.
Disavow The Remaining Bad Backlinks
Certain websites simply don’t reply.
It’s time to change tactics after attempting a few follow-up emails but not getting any answer.
Requesting that Google disregard a link is known as disavowing a link. Should the link disavow be effective, those malicious links will not be used against you.
Here is a step-by-step guide on disavowing backlinks:
To submit a disavow report to Google, you will need to create one. I make use of Monitor Backlinks for this.
It should be easy for you to choose which of your hyperlinks to disavow as you should already have a comprehensive list of them.

All that’s left to do is upload the report to Google. Just submit your file and use the Google Disavow Tool.

How Long Does It Take To Recover From A Google Penalty?
This is the big question.
Recovering from a Google penalty is tough and requires a lot of work. If you’re unsure about handling it yourself, I always recommend hiring a professional recovery service.
For manual penalties, expect to wait between ten and thirty days. This mainly depends on how quickly a Google team member reviews your changes. You can speed things up a bit by emailing them.
Algorithmic penalties are a different story. Recovering from these can take up to six months because many factors can affect it.
Your best bet is to focus on rebuilding trust with Google’s search algorithm. Check out our case study on how we helped a client recover from a Google core algorithm change for more insights.




Pingback: Overcoming Content Duplication Issues